Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
This is a page not in th emain menu
Published:
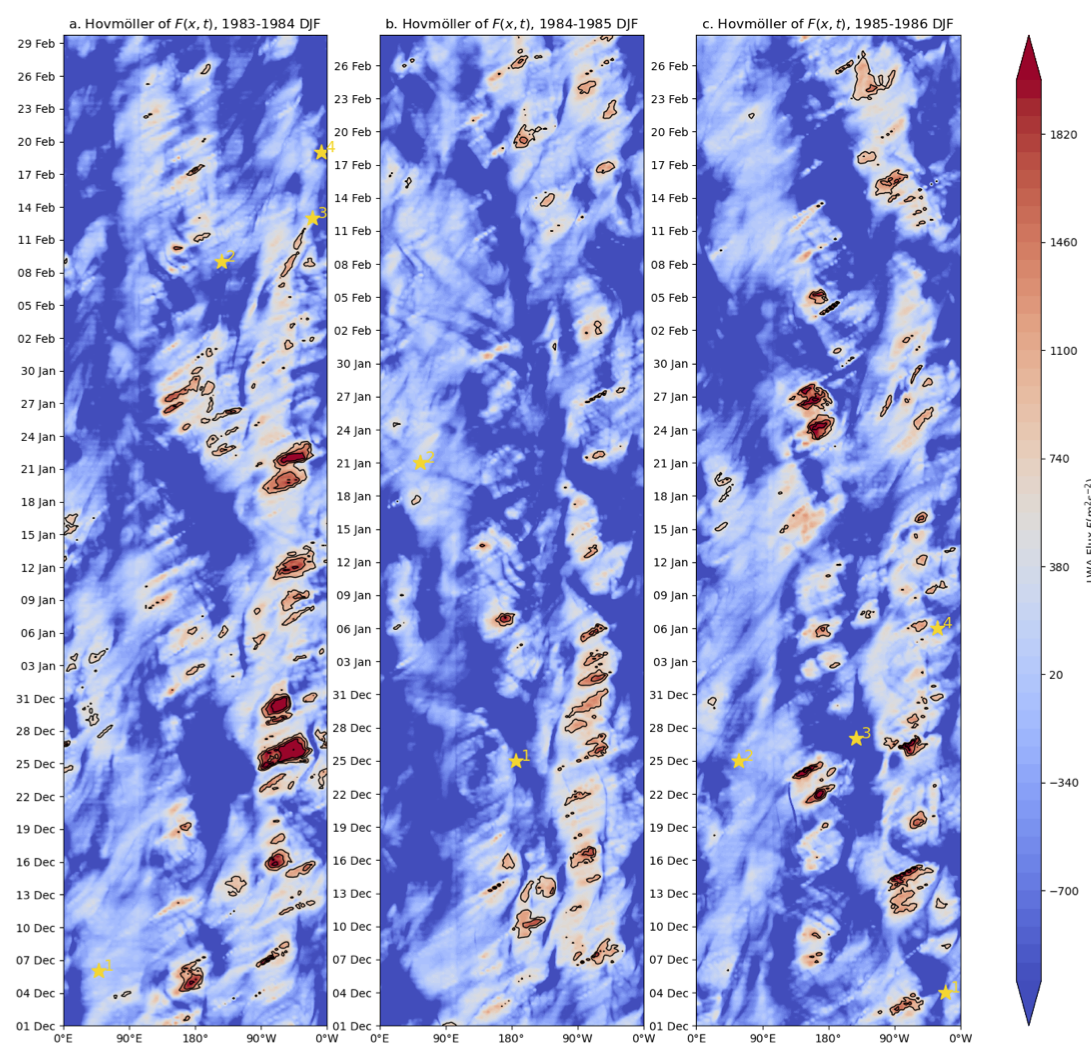
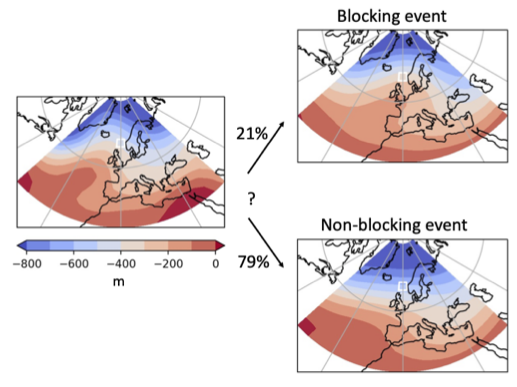
Xingjian (Ken) Yan, a precocious undergraduate (now bound for a PhD at MIT) working with Lei Wang and I just submitted a paper exploring the utility of the traffic jam theory of blocking onset for perdiction to Geophysical Research Letters. Ken defined and explored “flux exceedance events”, meteorological situations where the jet stream gets overloaded with storm activity. Nakamura and Huang suggested that this overloaded jet situation creates a pile up storm activity – a traffic jam – leading to blocking events. Ken found that the climatological structure of exceedance events is remarkably similar to that of blocks, but that they appear to be distinct phenomenon: an overloaded jet stream is unfortunately not a reliable harbinger of an atmospheric block.
Published:
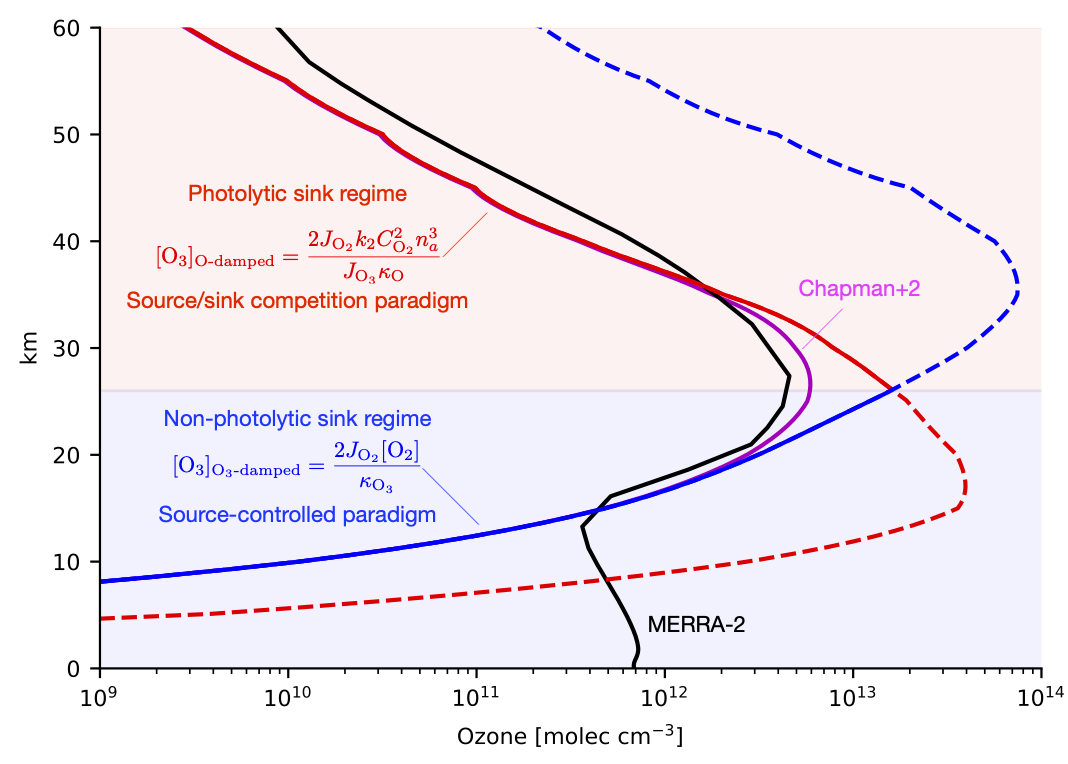
Aaron Match developed a new theory for why the ozone layer is up in the stratosphere, reaching a maximum 26 km above the surface in paper submitted to the journal of Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. In 1880, Walter Hartley deduced that ozone must be absorbing UV-B and UV-C radiation from the sun, but since it isn’t present at the surface (except in polluted air), this ozone must be somewhere “up there”. The stratosphere wasn’t discovered for a couple more decades, but it turns out that ozone that shields us from this harmful UV radiation is largely between 16 and 40 km above us. It’s a good thing its there: ozone is toxic. If it were uniformly distributed through the atmosphere, the concentration at the surface would be 8 times the EPA safety limit. Why is ozone safely up in the stratosphere, where it protects us without poisoning us? Advanced chemistry climate models can accurately predict the distribution of ozone, but in turns out our text book understanding of the ozone layer were incomplete and gave the wrong explanation for why it reaches a maximum in the stratosphere at 26 km.
Published:
Huan Zhang submitted our paper on how to use machine learning to predict the persistence of blocking events to the new Journal of Geophysical Research Machine Learning and Computation, published by the AGU. Blocking events are persistent high pressure systems that “block” the flow of the jet stream. They are associated with extreme weather, as they shift the direction of storms, and, in summer, create heat domes that drive heat waves. A key element of a block is its persistence. Huan developed a convolutional neural network to predict whether an nascent blocking anomaly would persist, or fade away, and then interrogated the network to understand why it worked, and how it could be trained with the short observational record.
Published:
Minah Yang submitted a paper on how to combat data imbalance in regression problems to JAMES. The goal is to improve the performance of data-driven paramterizations, particularly for profiles that are rare, but important. This is a data imbalance problem: we need ensure that the parameterization works well on input-output pairs that are seldom seen in training. Minah proposes a technique based on histogram equalization, visualized below with help from Cece, Minah’s faithful companion! The idea is to oversample or reweight these rare cases during training, to ensure the method learns from them.

Published:
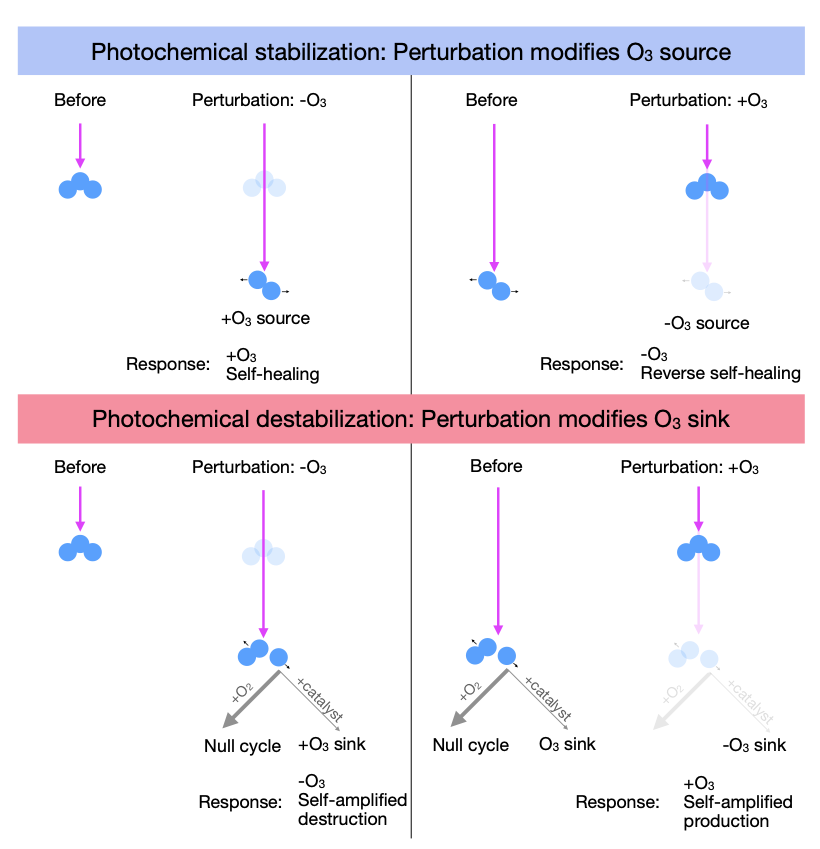
Aaron Match submitted a paper on how photochemistry can compensate or amplify perturbations to the ozone layer to journal of Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, published by the EGU. It has been observed that photochemistry can partially compensate for ozone loss due to CFCs and other ozone depleting substances. The process is known as self healing: decreases in tropical ozone aloft are associated with a counterintuitive increase at lower levels. It is not enough to fully compensate for the loss, but mitigates it. More recently, greenhouse gases have begun to cool the stratosphere, leading to increasing ozone aloft, which is partially compensated for by ozone reduction below (referred to as “reverse self healing”, which is admittedly a rather contorted phrase!). These responses are attributed to the fact that ozone loss increases the penetration of high energy UV radiation, which leads to more ozone production below (and skin cancer for us on the surface), vice versa for ozone increase due to cooling. Aaron asked whether this compensating response is generic, and found it is not! In upper stratosphere, photochemistry can amplify a perturbation, such that ozone loss would lead to more loss. But fortunate for us on the surface, compensation in the lower stratosphere is actually much more significant than appreciated before!
Published:
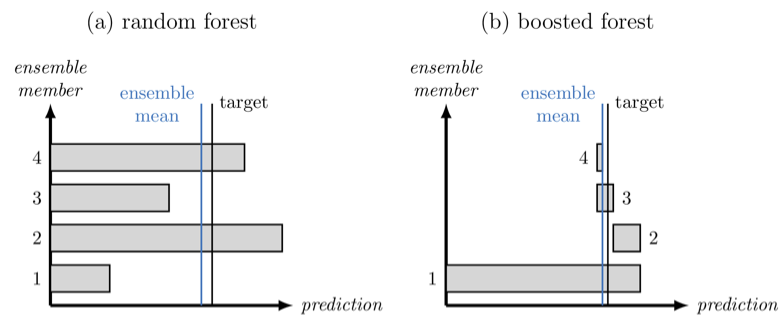
Congratulations to Dave Connelly, who just submitted his first paper! It is about the use of regression forest to represent atmospheric gravity wave momentum transport to JAMES! The manuscript makes two important steps forward. First, it shows that a “boosted forest” approach, where you train each subsequent decision tree on the residual (as sketched below), can out perform a “random forest” where you combine a number of decision trees, averaging the result. This was well known in the ML community, but less so in the climate sciences. Second, Dave found that techniques from interpretable AI could be used to improve the training of a data driven parameterization. Using feature importance metrics, he found that his origional boosted forest wasn’t using enough information about latitude. By forcing the method to predict the latitude as well, he could build trees that incorporate this information more effectively!
Published:
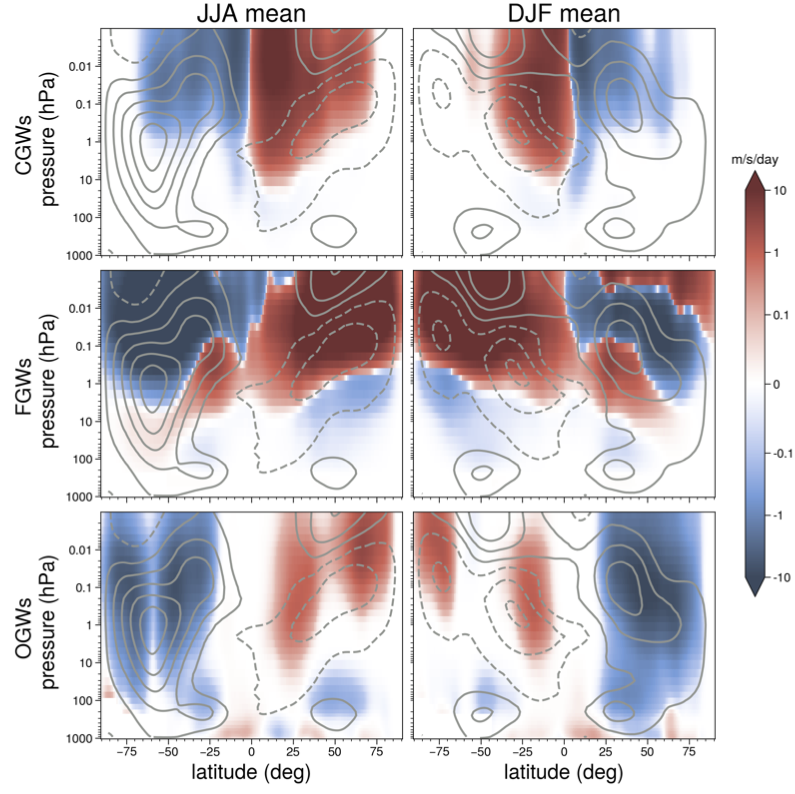
Don’t miss Y. Qiang Sun’s paper on the use of machine learning to emulate a physics-based atmospheric gravity wave parameterizations in a state-of-the-art climate model, in review in JAMES. It’s also up on the arxiv.
Published:
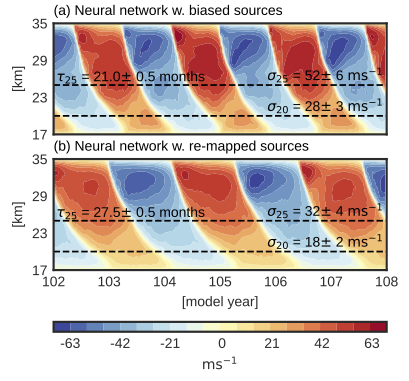
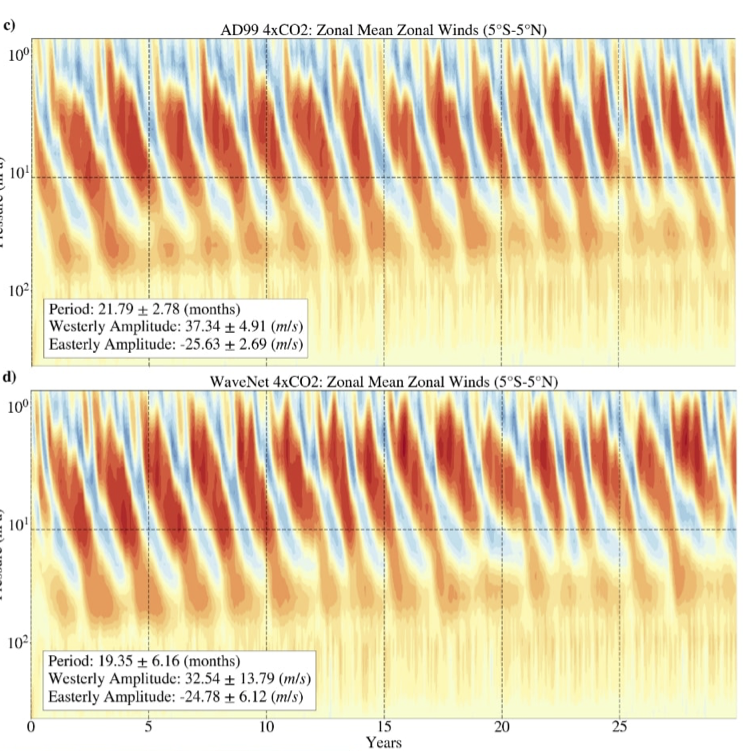
Ofer Shamir just submitted a paper on the use of machine learning to represent atmospheric gravity wave momentum transport to QJRMS. He developed an idealized, one-dimensional model of the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation, where we could systematically compare different data-driven methods. In particular, how can one calibrate a data-driven scheme to work in a biased model (the graft-host problem), and how well can schemes generalize to new conditions, as in a climate change scenario?
Published:
I flatter myself to think you may have stopped by my webpage over the last year and half and wondered, what happened to Ed? No new papers? No research? Did he drop off the face of the Earth? Sort of. I was on sabbatical at Free University Berlin and Ludwig Maximillian University, Munich for an academic year!

Published:
A number of group members are presenting work at upcoming meetings by the American Meteorological Society (AMS) and Society of Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM).
Published:
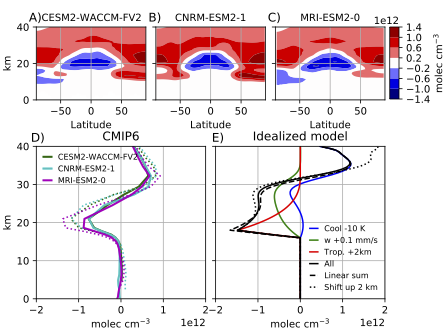
Aaron Match just submitted a very elegant paper on the impact of global warming on ozone in the tropical stratosphere to GRL! Combining the classic leaky pipe model of the stratosphere with Chapman photochemistry and a simple representation of tropospheric ozone destruction, we show that the apparant upward shift of ozone in response to global warming is actually due to fortituous overlap of several different processes.
Published:
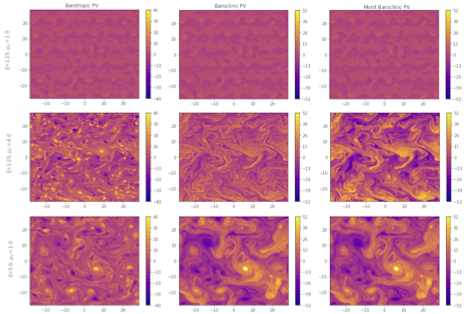
Marguerite Brown just submitted a very insightful paper on the role of moisture in the mid-latitude circulation to JAS! She builds on a pioneering work by Lapeyre and Held to use a moist 2-layer quasi-geostrophic model to tease out the competing roles of moisture and temperature in driving the midlatitude atmosphere.
Published:
Zac Espinosa’s study to replace a physics-based gravity wave parameterization with a neural network based emulator was just accepted in Geophysical Research Letters! 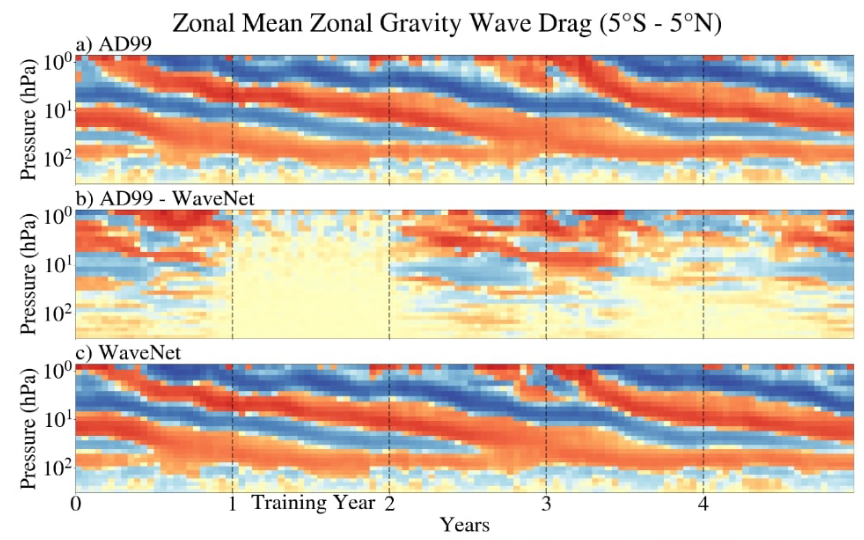
Published:
In a continuation of my collaboration with Chaim Garfinkel, Ian White, and Martin Jucker on the development of MiMA, and with long time colleague (and former office mate!) Seok-Woo Son, we’ve just submitted a paper to the Journal of Climate on the response of the troposphere to stratospheric ozone loss.
Published:
Following up on our initial submission last January, we’ve just resubmitted our paper on using machine learning to represent un(der)resolved gravity waves in atmospheric models.
Published:
The kitchen has been busy: two papers are now in press. First, Marianna Linz’s paper on mixing in the stratosphere was just accepted by the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. We show how the vertical gradients in age allow us to quantify the exchange of air between the tropics and extratropics. Increased mixing leads to better baking, right? In this case, it’s very important for transporting ozone and water vapor through the stratosphere, two trace gases that impact us on the surface, protecting us from UV radiation and keeping us a bit warmer, respectively.
Published:
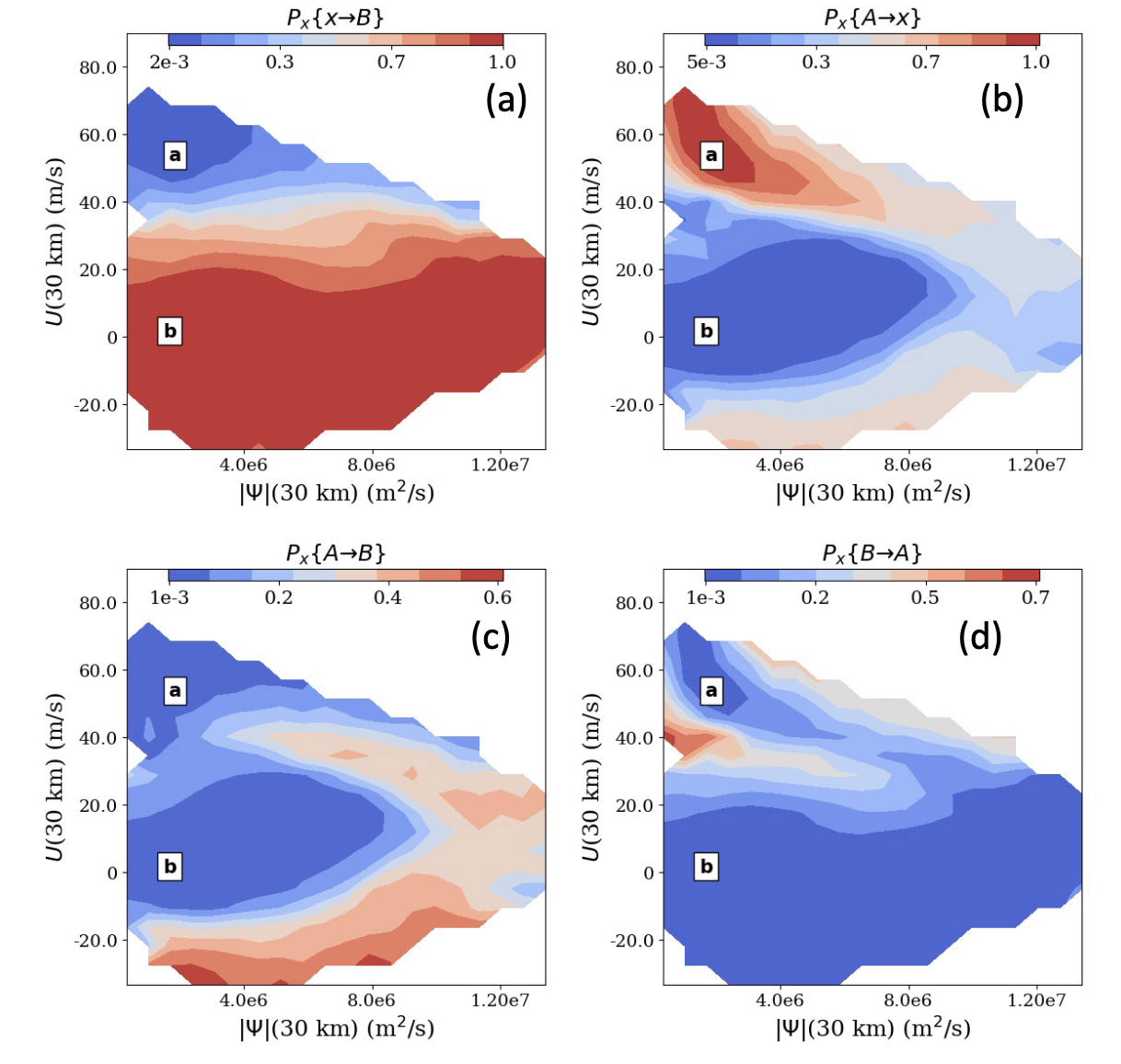
To conserve the number of papers in my queue, Justin Finkel submitted a new manuscript just as our MWR paper was accepted. Exploring stratospheric rare events with transition path theory and short simulations, submitted to the Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, takes a deeper dive into the idealized Holton and Mass (1976) model of Sudden Stratospheric Warming events using Transition Path Theory, TPT for short.
Published:
While I was returning from summer travels, the journals went into overdrive and three papers were accepted and/or came out in press!
Published:
The SPARC Reanalysis Intercomparison Project report has been published in an early online release! This has been nearly a decade in the making – I had only one child when I first got involved – but the long effort has really paid off. I am of course partial to Chapter 6, Extratropical Stratosphere-troposphere Coupling, but the entire report is full of information about the reanalyses and the stratosphere.

Published:
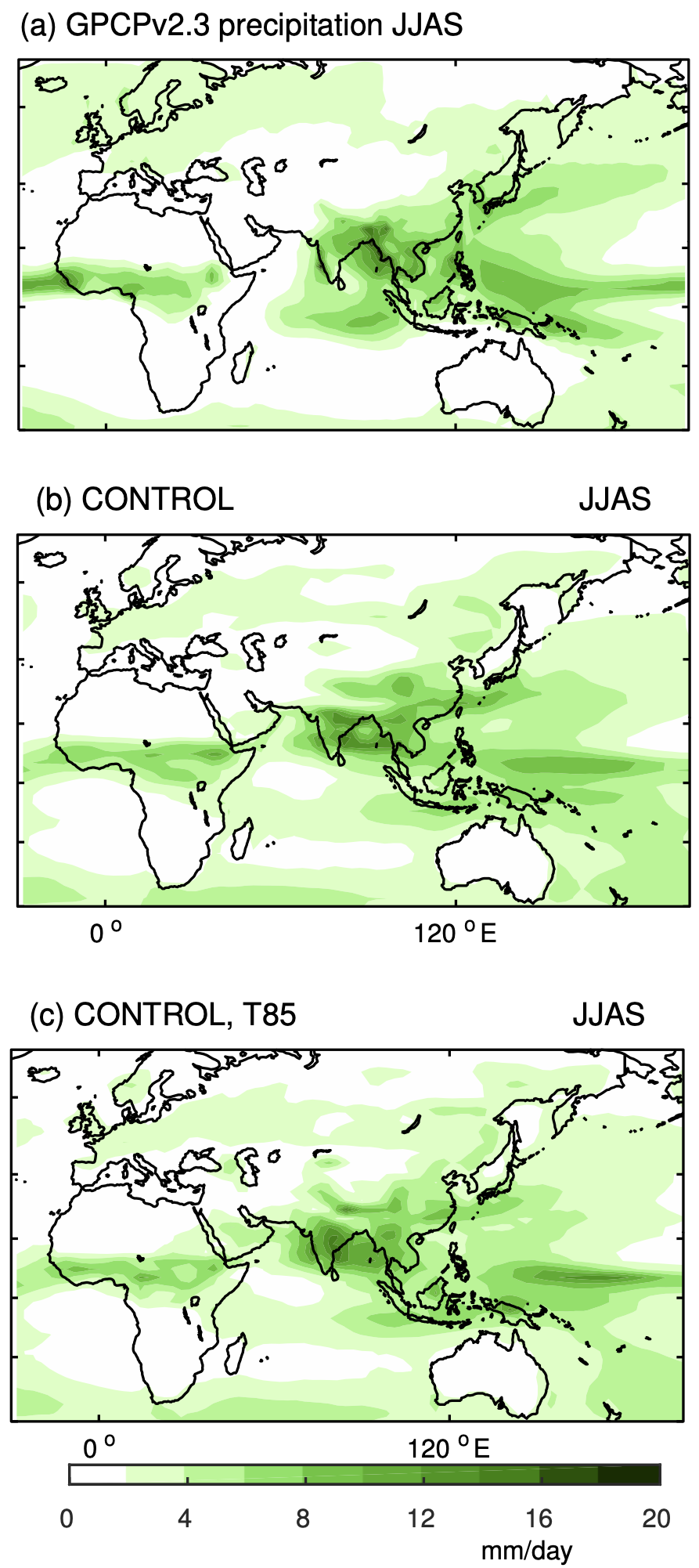
Our monsoon paper was just accepted for publication in Geophyiscal Research Letters. See my December post for more details.
Published:
Please see our paper exploring the role of “isentropic mixing” on the transport of trace gases through the stratosphere, just submitted to the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 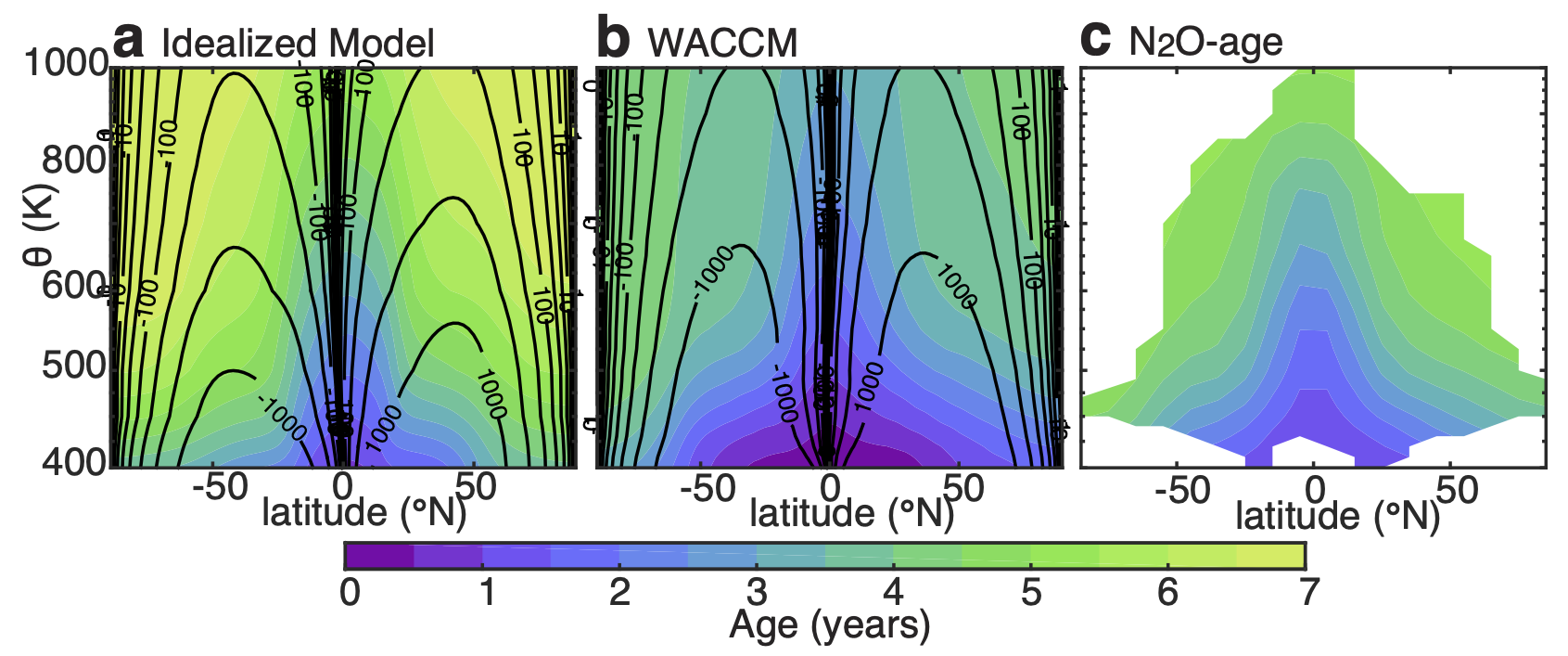
Published:
Please see our on the impact of stratospheric ozone loss on the atmosphere across the latest reanalysis products, just accepted in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. 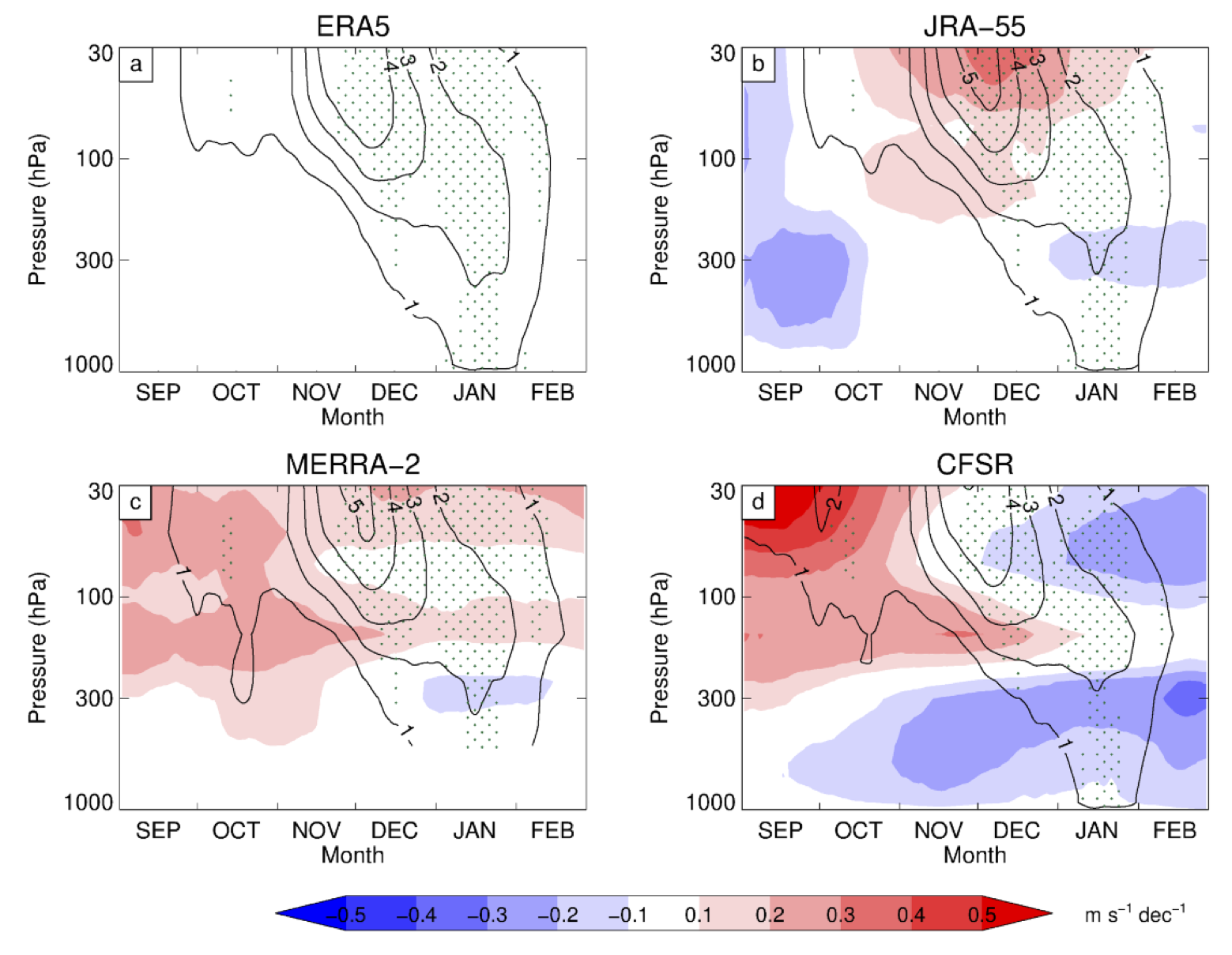
Published:
A fun article on NYU’s new Greene supercomputer and how it allows us to explore climate change came out in NYU IT’s Download Newsletter.
Published:
Please see our new paper providing a recipe for generating and optimizing a Quasi-Biennial Oscillation in your very own GCM, just submitted to JAMES. 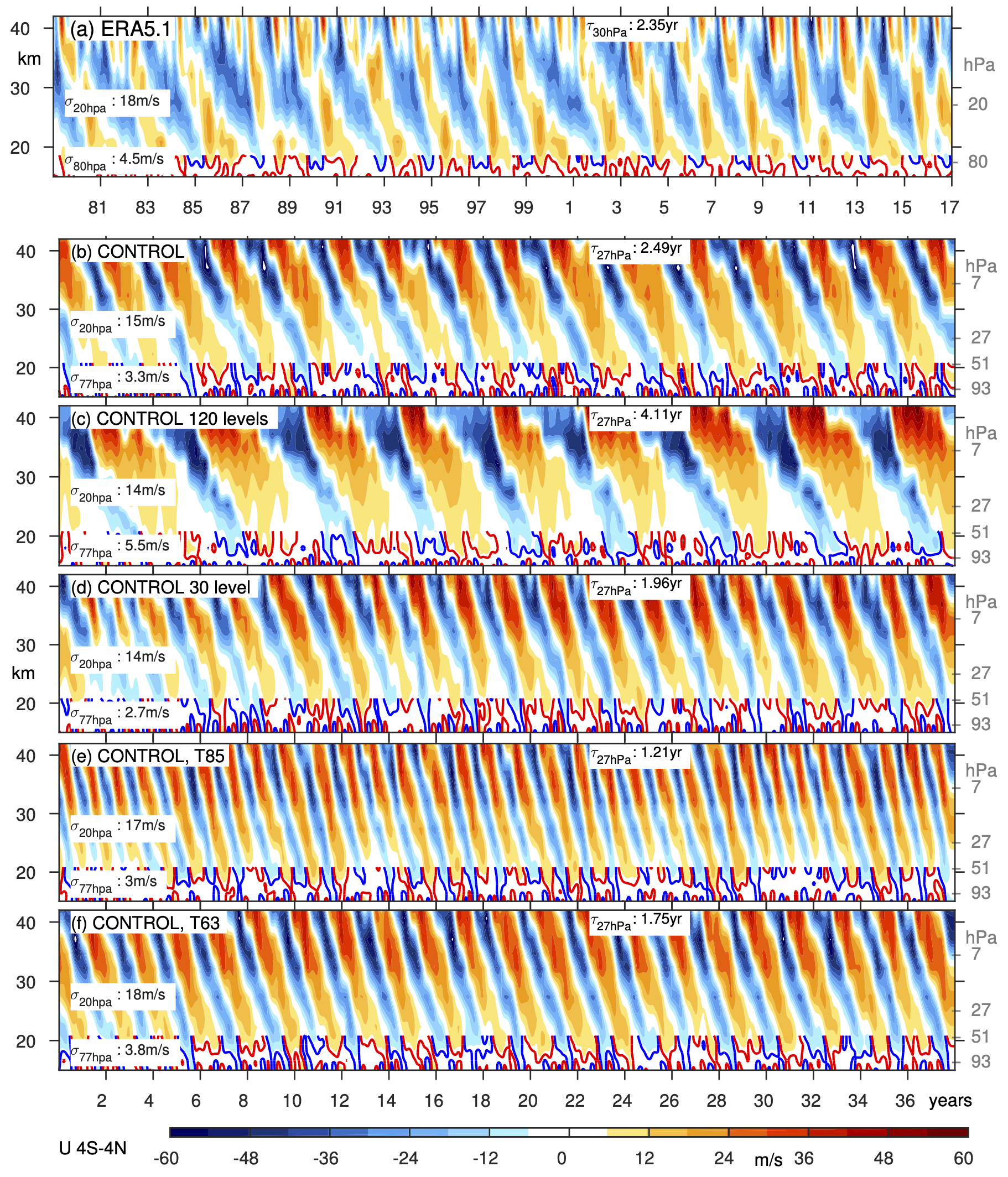
Published:
Check out our new paper exploring the origin of tracer transport biases in atmospheric models, just submitted to the Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 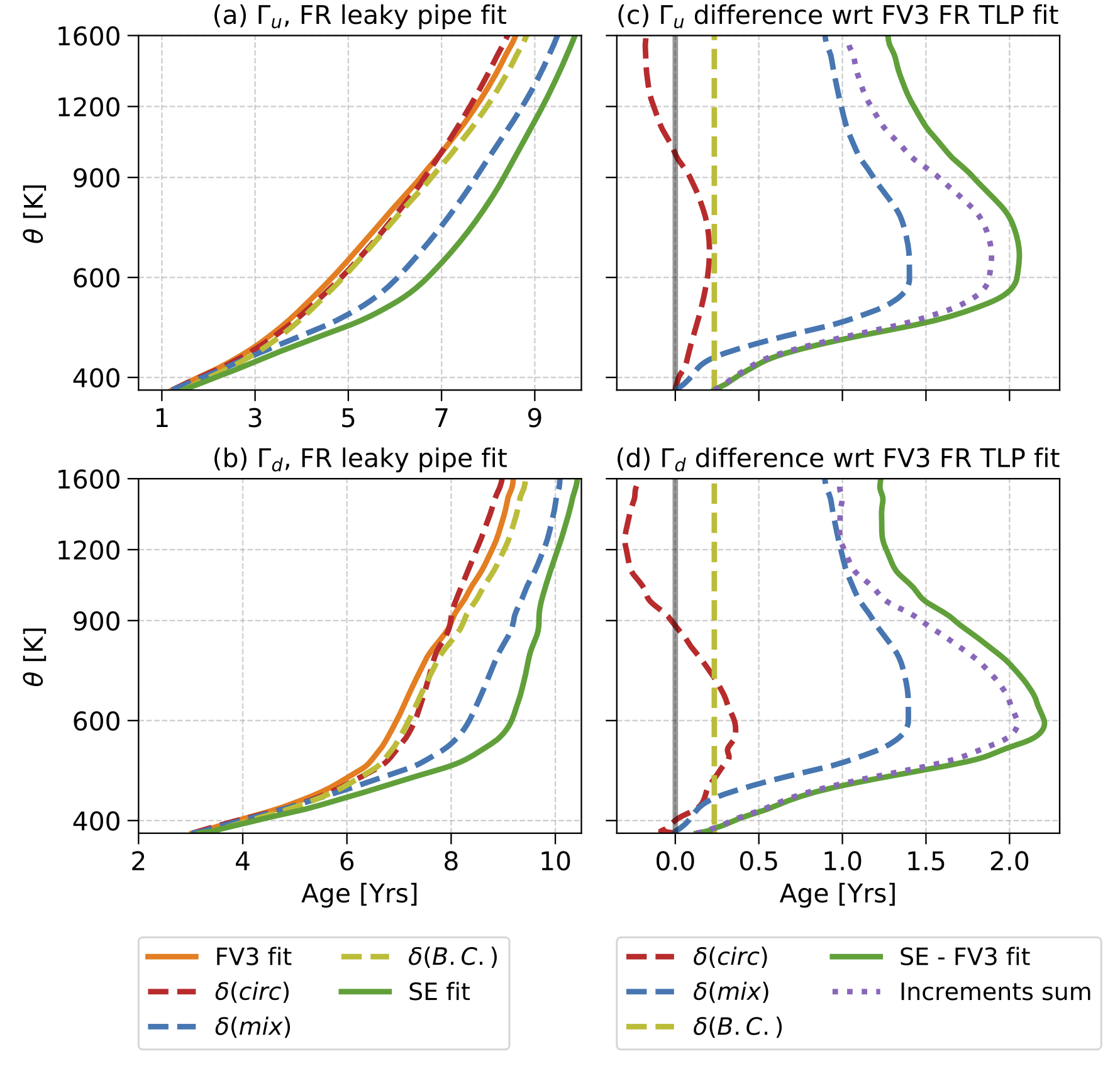
Published:
Please see our new paper adopting a novel prediction framework from computational chemistry to forecast extreme meteorological events, just submitted to Monthly Weather Review. The paper, led by Justin Finkel, presents a proof of concept study using a stochastically forced version of the classic Holton and Mass (1976) model of Sudden Stratospheric Warming events. We establish the “committor”, which provides the ideal combination of variables for predicting SSWs (where an SSW is a transition between the two fixed points in the Holton-Mass model). We also establish a method to compute it from relatively short integrations, i.e., integrations that are short relative to the time scale of the event, and much shorter than the return time scale of events. 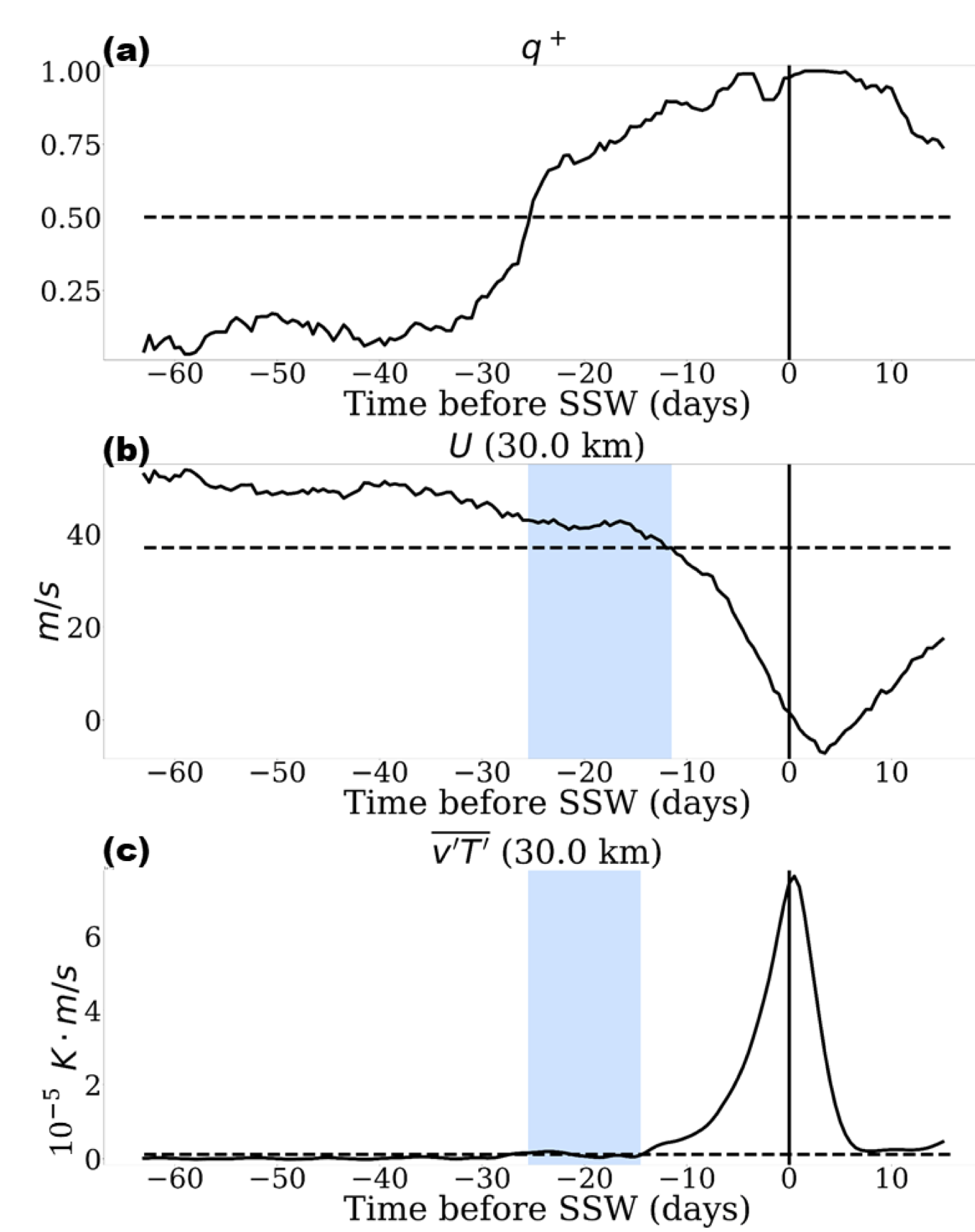
Published:
The newly minted Institute for Mathematical and Statistical Innovation has organized a virtual conference on climate change from 1-5 March, 2021. Speakers including experts in applied mathematics and climate research – and both, including my colleague Laure Zanna! It’s my understanding that the meeting is free to atttend, but that you must register in advance.
Published:
As my family and I cannibalize each other on our solitary descent into the abyss that is remote elementary education, intrepid collaborators will be hitting the virtual road to present at the vEGU this April! Check out these presentations:
Published:
Despite tremendous advances in our understanding of the atmosphere and our capability to simulate it with numerical models on the fastest computers in the world, their remain processes that we can not accurately represent from basic physical principles. In some cases, it is an issue of computational power: we cannot resolve all relevant scales for climate prediction, from planetary scale weather systems (10^6=1,000,000’s of meters) to cloud and aerosol particles on the microscale (10^-6=0.000001 m). In other cases, we do not yet know all the relevant physics! We still need to do our best to represent these processes based on what we can simulate. Traditionally this has been done with physically motivated schemes, but there’s growing in interest in using machine learning to help. Here we take the first steps of using an artificial neural network to help parameterize atmospheric gravity waves.
Published:
Suppose you could build your own planet: create continents, lift mountains, carve out the bathymetry of the ocean to help direct its currents! What would you need to do to create the monsoonal circulation on Earth, the sharp seasonal transitions in rainfall that play such a huge role in the climate of South and East Asia?
Published:
The short answer is: no! For a longer, more complete answer, please see our new paper on the representation of the stratospheric ozone hole on the Southern Hemisphere in the four latest atmospheric reanalyses, just submitted to Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics.
Published:
Our review article on Sudden Stratospheric Warmings, led by Mark Baldwin and Blanca Ayarzuguena, was just accepted for publication in Reviews in Geophysics. We’ve learned a great deal about “explosionartigen Stratosphärenerwärmungen” since they were first discovered by Prof. Dr. Scherhag almost 70 years ago!
Published:
A number of postdoctoral positions are available through a project funded by NSF’s Cyberinfrastructure for Sustained Scientific Inquiry (CSSI) program. This highly collaborative project between four institutions will develop data-driven parameterizations of atmospheric gravity waves and explore their impact on climate variability and change. The project will involve novel balloon-based observations, high-resolution atmospheric model simulations, machine learning, and atmospheric modeling.
Published:
I am aware that things have been rather quiet on my blog in the last months. In addition to my new found profession as an elementary school teacher (alas, not a very good one, but our efforts to get the kids transferred to another class were fruitless), we’ve been hard at work on revisions. Some very detailed and careful reviews allowed us to make two good papers even better!
Published:
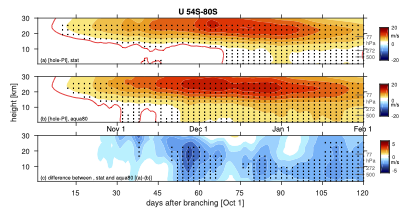
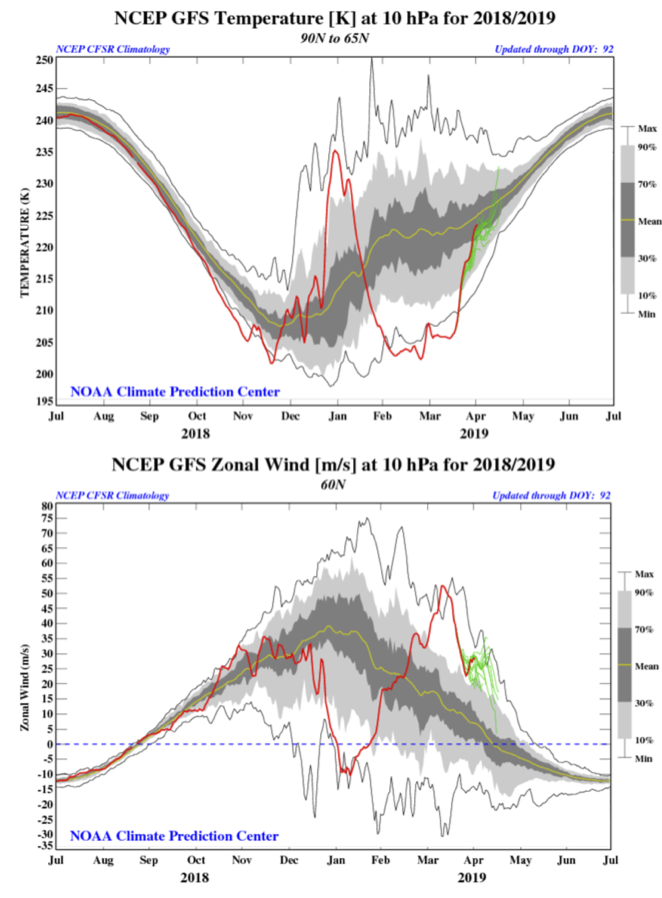
After a month in editorial system purgatory, just submitted to Geophysical Research Letters, our paper on “Downward migration of the zonal-mean circulation in the tropical atmosphere”, led by Kevin DallaSanta.
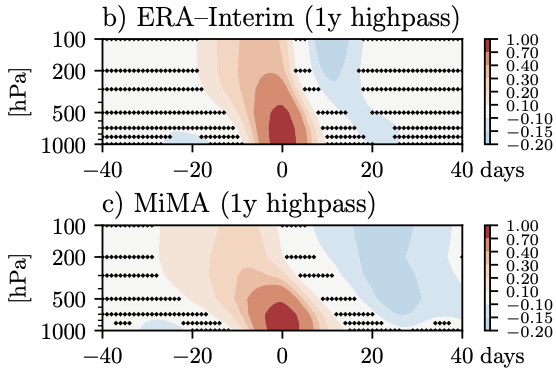
Published:
(*but were afraid to ask!) Please see our review paper, just submitted to Reviews of Geophysics, “Sudden Stratospheric Warmings”, led by Mark Baldwin and Blanca Ayarzuguena.
Published:
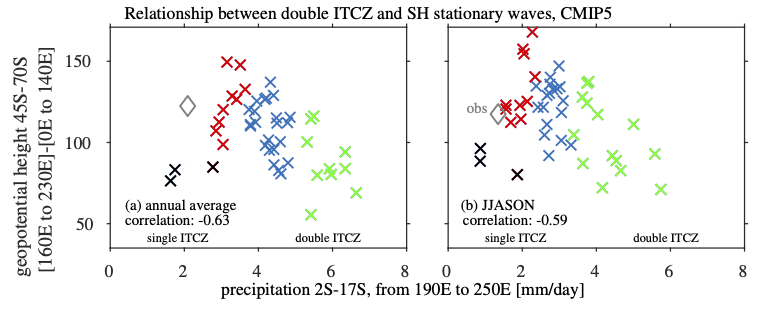
Just submitted to the Journal of Climate, our paper on “The impact of SST biases in the tropical east Pacific and Agulhas current region on atmospheric stationary waves in the Southern Hemisphere”.
Published:
A quick update on an earlier post: our paper exploring the impact of global warming stratosphere-troposphere coupling, was just accepted for publication in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. Look here for more details!
Published:
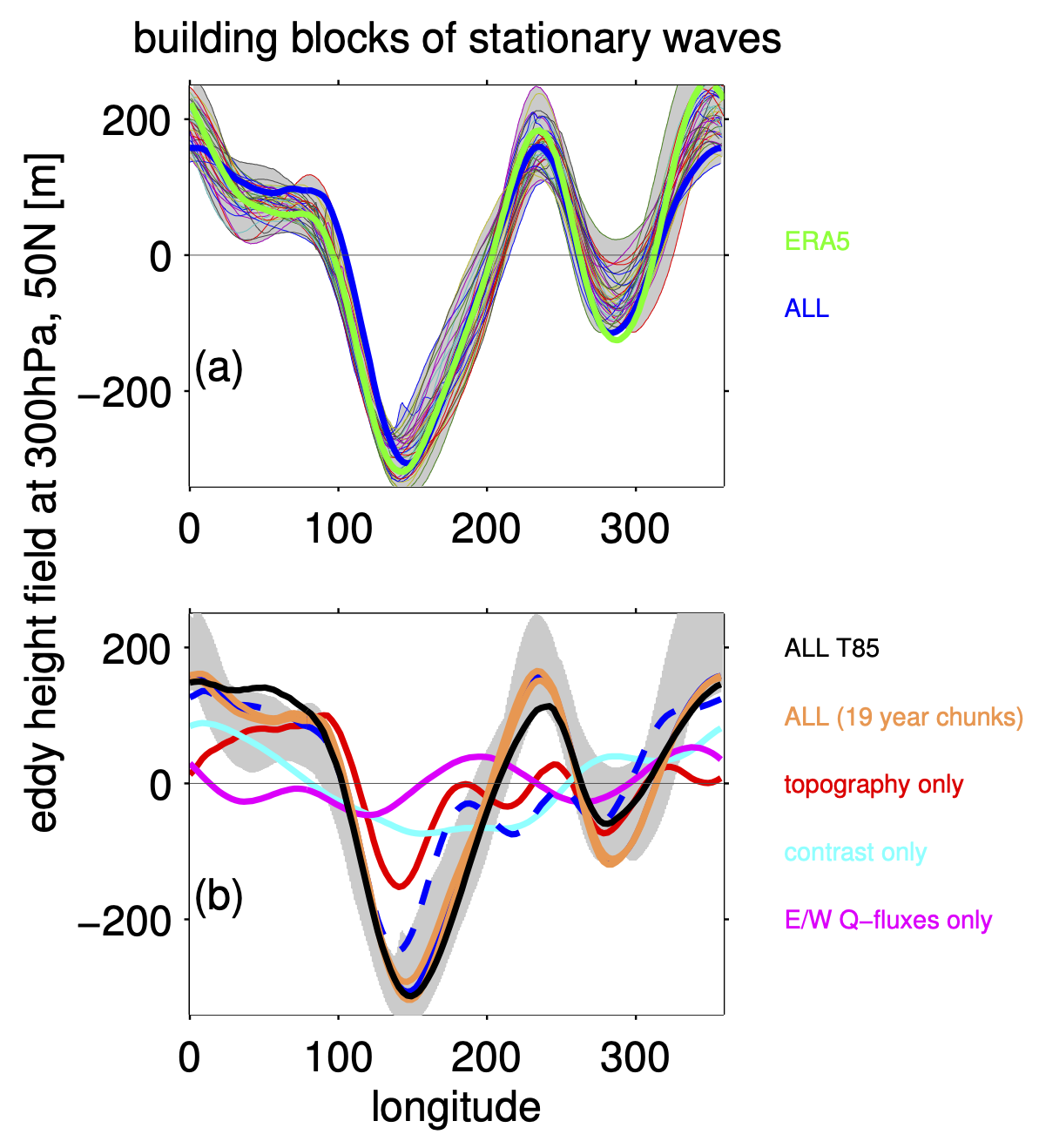
Please see our new paper exploring stationary waves in the Northern Hemisphere, just accepted in the Journal of Climate. What are stationary waves, you ask? In laymen’s terms, they are variations in climate with longitude, for example, the reason why the weather in Madrid is quite different from that here in New York, even though we’re both situated at nearly the exact same latitude.
Published:
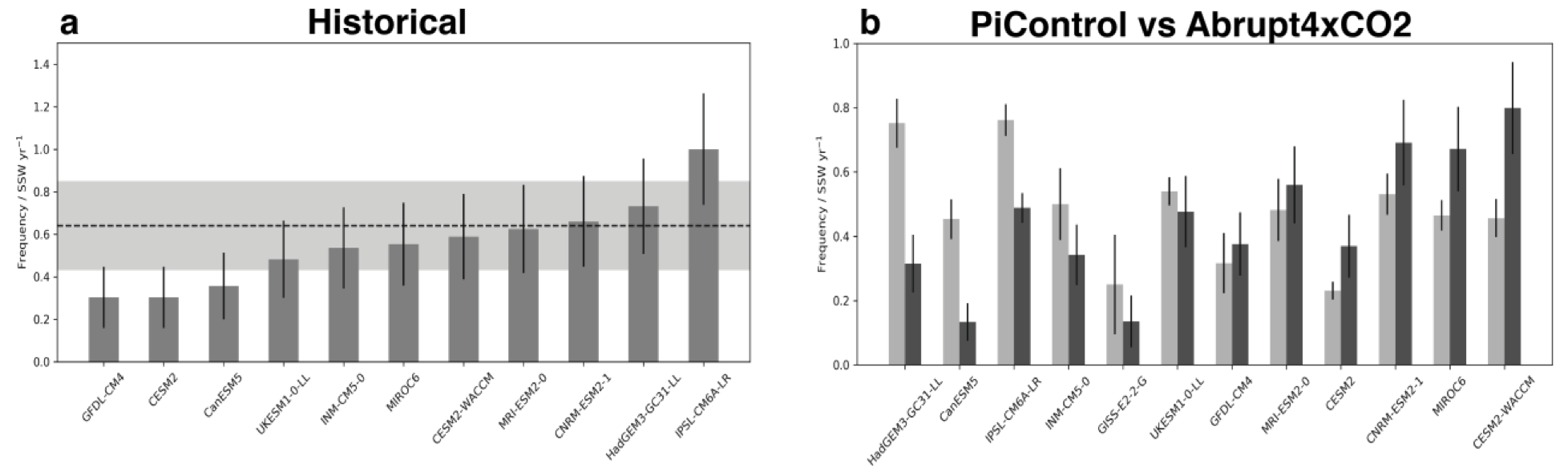
Please see our new paper exploring the impact of global warming stratosphere-troposphere coupling, just submitted to the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres.
Published:
Aman Gupta is defending his thesis on Wednesday 18 December at 1:15 in Warren Weaver 1302. Come see the world’s leading expert on trace gas transport through the stratosphere by the dynamical cores of atmospheric models!
Published:
Please see our new paper exploring the role of model numerics on trace gas transport, just submitted to the Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society.
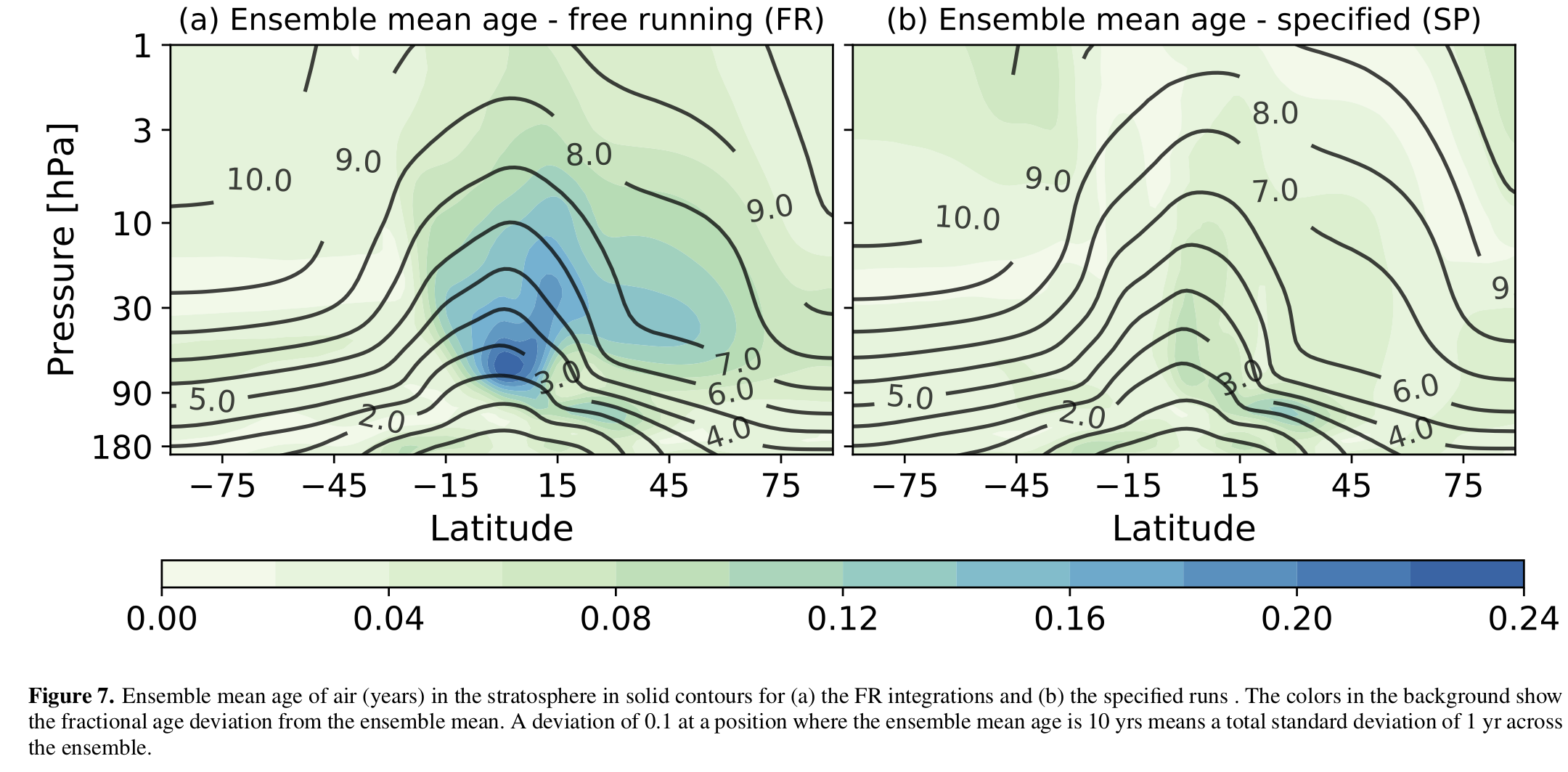
Published:
Please see our new paper on the tropospheric response to extreme events in the stratosphere, just submitted to the Journal of Climate. Update: this paper was accepted for publication in January 2020!
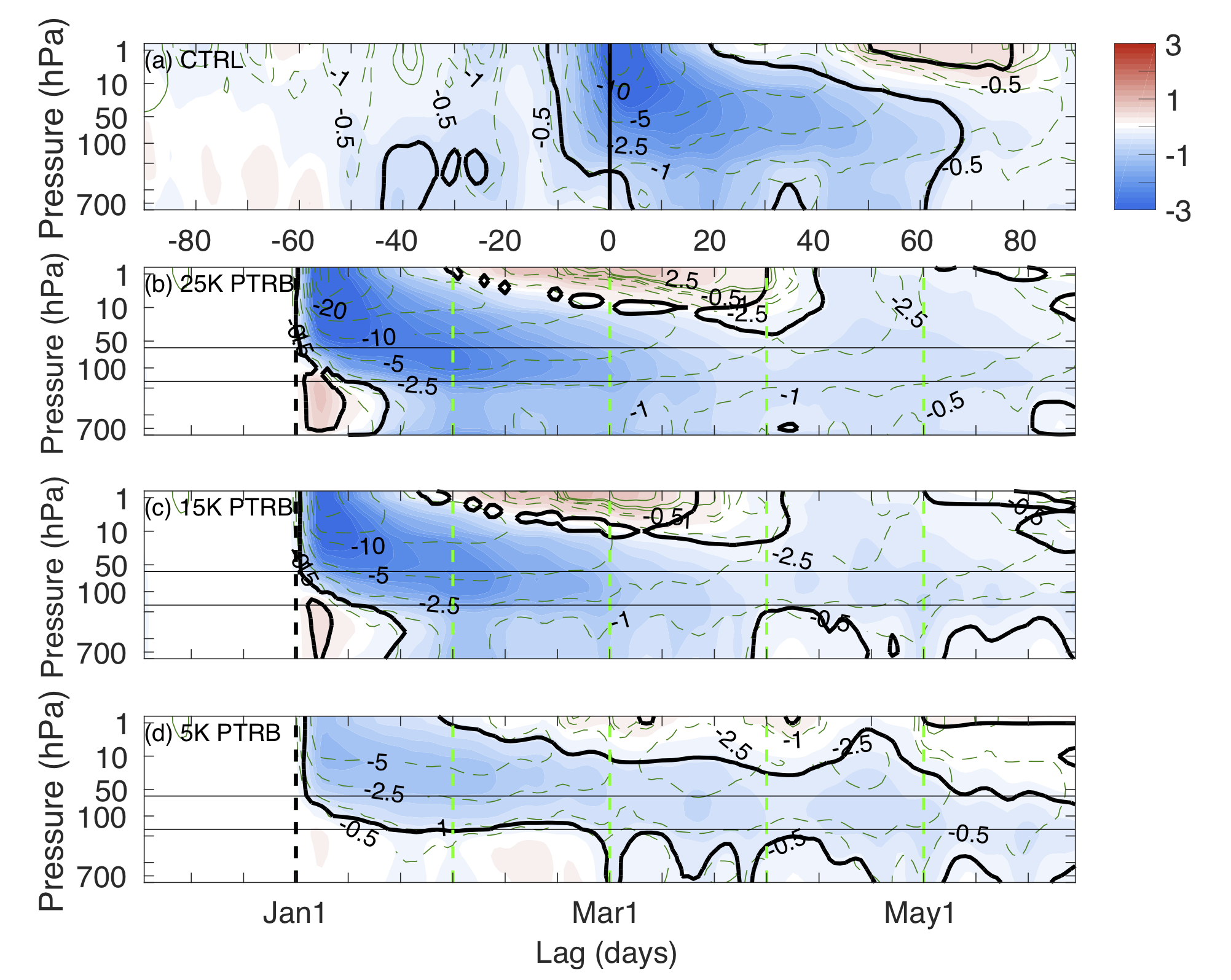
Published:
Our commentary for the Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, “Imagining Simpler Worlds to Understand the Complexity of our Own”, was just accepted for publication. It follows on a nice paper by Zhihong Tan, Orli Lachmy, and Tiffany Shaw that recently appeared in the same journal.
Published:
Please see our chapter on extratropical stratosphere-troposphere coupling, just submitted as Chapter 6 of the SPARC Reanalysis Intercomparison Project, S-RIP. I’m quite pleased by the final (or at least, submitted) product! Kudos to Patrick Martineau, my co-lead on this 17 author effort which started over 6 years ago. Six years ago, a far away time when I only had one kid. To say that I’m very relieved to have this submitted is an understatement!
Published:
An updated on our workshop on the Atmospheric Circulation in a Changing Climate, 22-25 October 2019, Madrid, a joint DynVarMIP, SPARC DynVar, and SNAP meeting, hosted by Universidad Complutense Madrid, Instituto de Geociencias.
Check out our line up of invited speakers!
Published:
Just submitted to JAMES: our commentary on a nice paper by Zhihong Tan, Orli Lachmy, and Tiffany Shaw that recently appeared in the same journal. We make the case that models of simpler atmospheres – which are distinct from simple models of our atmosphere – can help us understand the circulation response of our atmosphere to global warming, and enable us to build better climate prediction models!
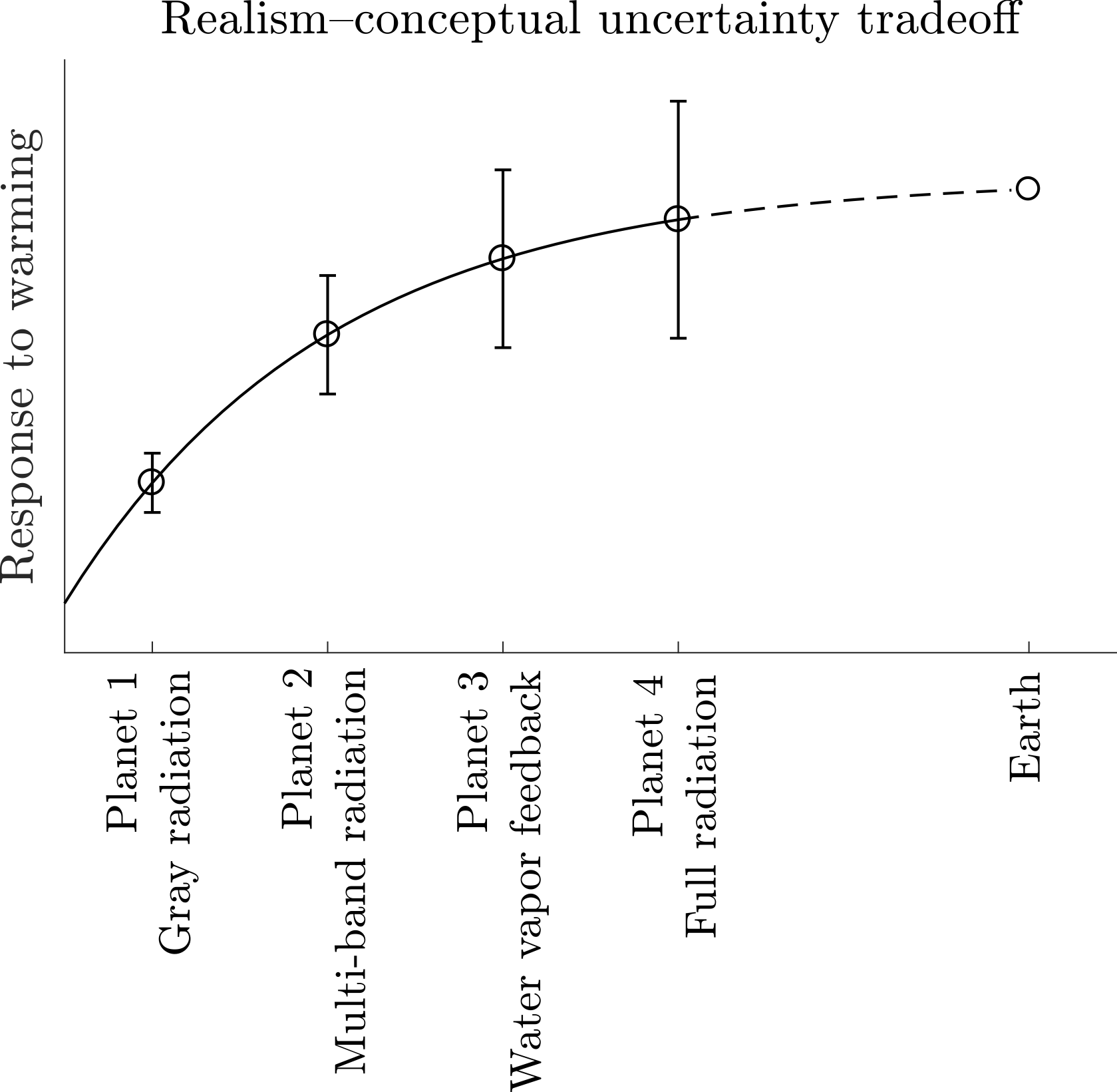
Published:
Please come to our workshop on the Atmospheric Circulation in a Changing Climate.
22-25 October 2019, Madrid
A joint DynVarMIP, SPARC DynVar, and SNAP meeting, hosted by Universidad Complutense Madrid, Instituto de Geociencias. A substantial amount of travel support is available for Early Career Scientists and participants from underrepresented nations!
Published:
Our manuscript for Reviews of Geophysics, Model hierarchies for understanding atmospheric circulation, was just accepted! Way to go Penny! In particular, I like our new figure illustrating the web of models around state-of-the-art Atmospheric General Circulation Models (AGCMs). These hierarchies of simpler models enables us to understand and improve our weather and climate prediction systems. 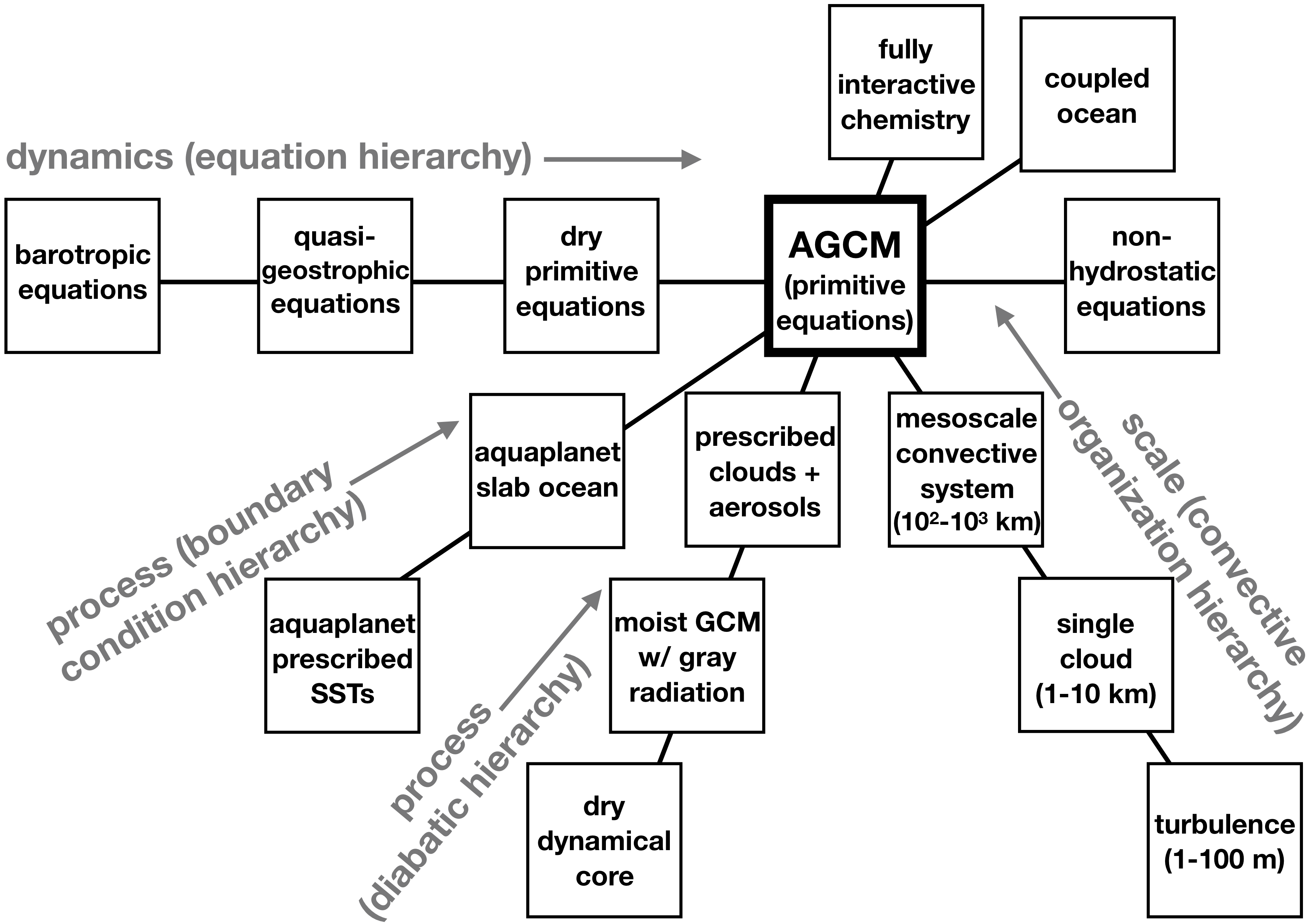
Published:
While Rome and New York receive the same amount of energy from the sun (being situated at the same latitude), the former experiences a much warmer climate, particularly in the winter months. This is due to large variations in the atmospheric flow with longitude, known as “stationary waves”. It has long been known that these variations are generated by differences between land and sea, topography, and variations in sea surface temperatures. But just how do these different components add up to produce our climate?
Published:
The whole group is hitting the road. Check out talks in Boulder, Palo Alto, and uptown, to be helf over the next couple weeks!
Published:
Coming to the AMS Annual Meeting in Phoenix next week (6-10 January)? Check out these presentations!
Published:
Please see our paper Quantifying the variability of the annular modes: Reanalysis uncertainty vs. sampling uncertainty, just accepted in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. Patrick Martineau and I show that reanalyses have gotten quite good, and we are chiefly limited by the finite length of the observational records. In this sense, we are starved for data, not model physics!
Published:
Deterministic weather forecast are only possible for one to two weeks. (Or in other words, we just can’t predict whether it will be sunny or rainy 14 days from now.) But can we say something about the weather over the next few weeks, for example, will it be warmer and drier than average, even if we can’t say exactly which days will be sunny?
Published:
Why do some Sudden Stratospheric Warmings appear to influence the troposphere, shifting the jet stream equatorward over the next 2-3 months, while others don’t? Much of the issue is tropospheric variability, which can overwhelm the influence of the stratosphere. However, our recent study, The Downward Influence of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings: Association with Tropospheric Precursors shows that there are regional patterns that can help us predict whether a Sudden Warming is more likely to have an influence on the troposphere!
Published:
Aman is a PhD student in my group.
Published:
Kevin is a PhD student in my group.
Published:
Postdoctoral Research Scientist, 2014-2016.
Official Version to appear.
Official Version to appear.
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
The transport of trace gases through the stratosphere impacts surface climate. Small changes in stratospheric water vapor, on the order of one part per million, can impact surface temperature by as much as a tenth of a degree. A sudden drop in stratospheric water vapor of this magnitude – a response to internal variability of the atmosphere – was observed in 2000. Chemistry climate model simulations of stratospheric ozone also depend critically on the transport of ozone and ozone depleting substances, and biases in transport are a leading source of uncertainty in the recovery of stratospheric ozone. Volcanic aerosols (and the possibility of injecting sulfur into the stratosphere for climate intervention) provides another example of the importance of stratospheric tracer transport for the climate at the surface.
Published:
The annular modes of the extratropical atmosphere have received much attention for quantifying and predicting variability of the jet streams and storm tracks, despite the limited zonal coherence of midlatitude variability. In the tropics, annular Huctuations of the circulation have not been investigated, despite the comparative dominance of zonal-mean variations in this region, associated with weak temperature gradients at low latitudes.
Published:
This is my first ever virtual colloquium visit. From the comforts of my own office, I’ll present my talk over the internet, coupled with a day of virtual meetings with students, postdocs, and faculty. The goal is to reduce our CO2 footprint – something our field should mindful of more than any other – but it will also help reduce the “family footprint”, i.e. the impact on spouses left to deal with kids who tend to get sick this time of year. Ugh. Only catch is that the seminar is 3:30 pm on a Friday, Pacific time!
Published:
Postponed due to COVID-19.
Published:
A virtual visit to Korea, giving me the chance to speak into the future. My talk will be Thursday 8 October at 9 am for the audience, 8 pm on Wednesday for me!
Published:
A virtual visit to Israel…
Published:
A virtual presentation this year. A pre-recorded talk plus 4 minutes of discussion at 11:30 pm, EST. O brave new world, with such meetings in it!
Published:
A virtual visit to London…
Published:
This virtual conference was organized by the newly minted Institute for Mathematical and Statistical Innovation.
Published:
I finally made it to Harvard, in spirit if not in person. A virtual visit, but quite productive!
Published:
An outreach seminar directed at NYU undergraduates interested in applied mathematics and climate science.
Published:
I attended this meeting virtually, actually tuning in from three different locations. In a classic, left hand doesn’t know what the right is doing, I managed to schedule our moving date to Berlin to coincide with my talk! It only worked out in the end because our sessions were in the late afternoon in Pittsburgh, so I could join our sessions at 10 pm. It started on the last day of our vacation in Tuscany, then I was in Bayreuth for the second day, as we paused on our drive across Europe, reaching Berlin for the final day of the symposium when I gave my talk!
Published:
My first in person meeting since AGU 2019! The Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach is a wonderful mathematics retreat center, library, and research institute tucked away in the Schwarzwald (Black Forest).
Published:
Here’s the poster.
Published:
My first in-person seminar since April 2019!
Published:
The first stop on my 2022-3 tour of Germany.
Published:
A seminar and visit to meet with collaborators in Frankfurt.
Published:
A talk down south while I’m meeting with colleagues at LMU and DLR.
Published:
A talk and opportunity to meet with more collaborators on our DataWave project.
Published:
Another talk while in town, and opportunity to meet with collaborators on the Isca Modeling Hierarchy, and see my PhD advisor.
Published:
A ‘solicited’ talk at the 2023 EGU Meeting at a session on the middle atmosphere. Hmm, sounds a bit sketchy in American English, where solicited usually comes up in a legal context! I’m taking it as an opportunity to show Justin Finkel’s methods to extract climatological statistics from S2S data. This is joint work with Dorian S. Abbot and Jonathon Weare.
Published:
A contributed talk at the 2023 EGU Meeting at a session on dynamics and predictability on subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) time scales. I’m presenting work led by my former postdoc, Madeleine Youngs, in collaboration with my colleague Olivier Pauluis.
Published:
A short tour of Schweiz, beginning at the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich!
Published:
The colloquium in Climatology, Climate Impact and Remote Sensing at the Universität Bern is another opportunity to show Justin Finkel’s methods to extract climatological statistics from S2S data. This is joint work with Dorian S. Abbot and Jonathon Weare.
Published:
The third and final stop on my tour of Suisse, catching a bit of the French speaking part!
Published:
I presented Justin Finkel’s methods to extract climatological statistics from S2S data at the Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique (LMD). It’s joint work with Dorian S. Abbot and Jonathon Weare.
Published:
A second stop on my short Tour de France.
Published:
I’ll be presenting Justin Finkel’s methods to extract climatological statistics from S2S data at the KlimaCampus Colloquium, a joint seminar series between the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology and the University of Hamburg. This is joint work with Dorian S. Abbot and Jonathon Weare.
Published:
I’ll be presenting Justin Finkel’s methods to extract climatological statistics from S2S data at the physics department colloquium, rounding out my series of visits to LMU and DLR over my sabbatical. This is joint work with Dorian S. Abbot and Jonathon Weare.
Published:
To round out my sabbatical, an invited talk at the 2023 International Union of Geodosy and Geophysics General Assembly. Fitting that the meeting is in Berlin! As in Vienna, I’m taking it as an opportunity to show Justin Finkel’s methods to extract climatological statistics from S2S data to an audience of atmospheric scientists. This is joint work with Dorian S. Abbot and Jonathon Weare.
Published:
I gave this talk in place of Ofer Shamir, who had just been traveling to another meeting in Wien.
First Year Seminar, Fall, 2018
Thursdays, 2:00-4:30, Warren Weaver Hall 1314
Office Hours: Wednesday 2-3 pm and Thursday 1-2 pm, Warren Weaver Hall 911
MATH-UA 228 / ENVST-UA 360, Spring, 2019
Lectures: Monday and Wednesday, 9:30-10:45, Warren Weaver Hall 312
Laboratory: Friday, 9:30-10:45, Warren Weaver Hall 517
Office Hours: Monday and Wednesday, 11-12, Warren Weaver Hall 911
First Year Seminar, Fall, 2019
Thursdays, 2:00-4:30, Warren Weaver Hall 1314
Office Hours: Wednesday 2-3 pm and Thursday 1-2 pm, Warren Weaver Hall 911
MATH-GA 3004, Spring, 2020
Lectures: Tuesday 1:25-3:15 pm, Warren Weaver Hall 512
Office Hours: Tuesday 3:30-4:30 and Wednesday 2:30-3:30, Warren Weaver Hall 911
MATH-UA 262, Fall, 2020
Lectures: Monday and Wednesday 2:00-3:15 pm, online
Office Hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00 pm and Wednesday 8:30-9:30 pm, online
MATH-GA 3011, Spring, 2021
Lectures: Thusday 9:00 - 10:50 am Eastern Time (New York) on Zoom.
Office Hours: By appointment
MATH-UA 262, Fall, 2021
Lectures: Monday and Wednesday 2:00-3:15 pm, Kimmel 914
Office Hours: Monday and Tuesday 3:30-4:30 pm, Warren Weaver 911
MATH-UA 262, Spring, 2022
Lectures: Monday and Wednesday 9:30-10:45 pm, Warren Weaver 512
Office Hours: Monday 1:30-20:30 pm and Wednesday 11:00 am - 12:00 noon (Virtual)
MATH-UA 262, Fall, 2023
Lectures: Monday and Wednesday 2:00-3:15 pm, Warren Weaver 102
Office Hours: Monday and Tuesday 3:30-4:30 pm, Warren Weaver 911
MATH-GA 3004, Spring, 2024
Lectures: Tuesday and Thursday 3:30-4:45 pm, Warren Weaver Hall 517
Office Hours: Friday 10:00-12:00, Warren Weaver Hall 911